设计模式之命令模式
命令模式将“请求”封装成对象,以便使用不同的请求、队列或者日志来参数化其他对象,命令模式也支持可撤销的操作。
来解析这个定义:
- “将一个请求封装为一个对象”,请求原本是一个方法,现在要封装成一个对象,说明要新增类来完成。
- “可以用不同的请求对客户进行参数化”,说明是将命令对象作为参数进行传递。
- “队列”说明需要维护命令多个命令的列表队列。
- “撤销”说明有命令对象有undo撤销方法。
命令模式在设计模式中,算是一个比较不好理解的模式,很重要的原因是不清楚设计意图,不清楚不用这个模式前有何问题,这个模式带了哪些好处,能解决什么问题。
上一篇状态模式中,看到了状态模式抽离的是状态(属性),向上提成状态对象。有了这个基础,再来理解命令模式就相对简单了。命令模式抽离的是行为(方法),向上提成命令对象。
两者都通过“对象化”来解耦和扩展系统,但解决的问题不同:
- 状态模式:处理对象内部状态驱动的行为变化。
- 命令模式:处理行为请求的封装与调度。
我们直接在遥控器类中硬编码控制逻辑。
// 遥控器类(紧耦合,难以扩展)
class RemoteControl {
private Light light;
private Fan fan;
public RemoteControl(Light light, Fan fan) {
this.light = light;
this.fan = fan;
}
// 直接调用设备方法
public void pressLightButton() {
if (light.isOn()) {
light.off();
} else {
light.on();
}
}
public void pressFanButton() {
if (fan.isOn()) {
fan.off();
} else {
fan.on();
}
}
}
// 灯类
class Light {
private boolean isOn = false;
public void on() { isOn = true; System.out.println("Light is ON"); }
public void off() { isOn = false; System.out.println("Light is OFF"); }
public boolean isOn() { return isOn; }
}
// 风扇类
class Fan {
private boolean isOn = false;
public void on() { isOn = true; System.out.println("Fan is ON"); }
public void off() { isOn = false; System.out.println("Fan is OFF"); }
public boolean isOn() { return isOn; }
}
// 客户端代码
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Light light = new Light();
Fan fan = new Fan();
RemoteControl remote = new RemoteControl(light, fan);
remote.pressLightButton(); // Light is ON
remote.pressFanButton(); // Fan is ON
remote.pressLightButton(); // Light is OFF
}
}这个实现中,遥控器直接依赖 Light 和 Fan,新增设备(如空调)必须修改 RemoteControl 类。每增加一个设备,就要在 RemoteControl 中添加新方法(如 pressACButton())。
还有一个重要的点,无法支持撤销/重做,没有记录操作历史的能力。这个是命令模式非常重要的设计意图。
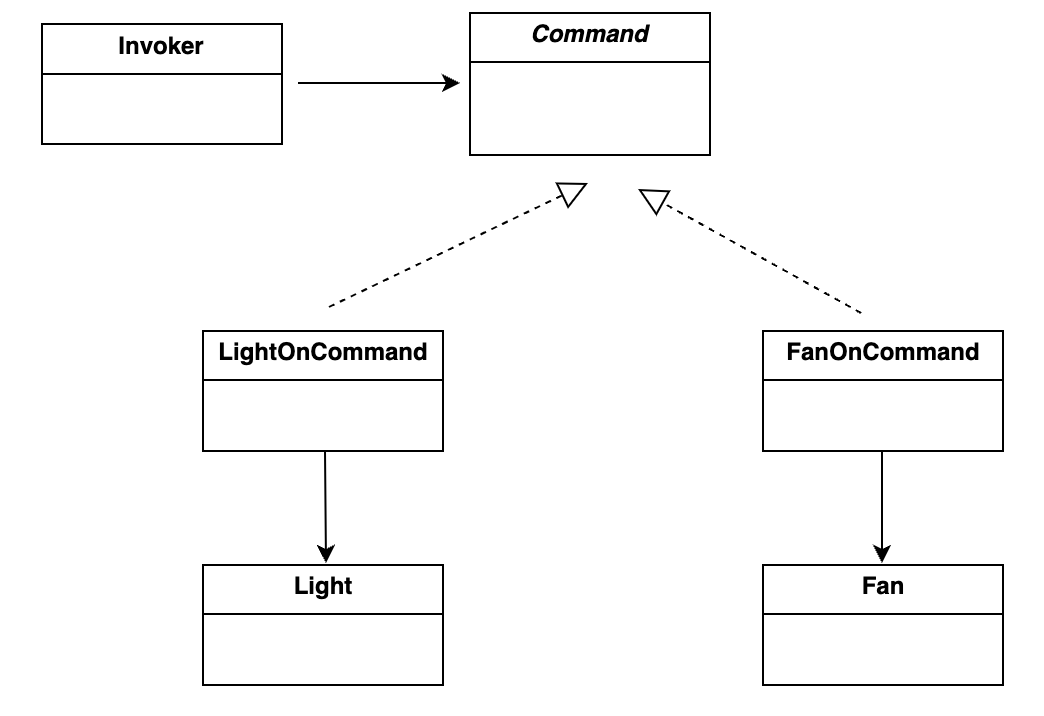
我们引入 命令模式,将每个操作封装成独立的 Command 对象:
定义命令接口。
interface Command {
void execute();
void undo(); // 支持撤销
}实现具体命令。
// 开灯命令
class LightOnCommand implements Command {
private Light light;
public LightOnCommand(Light light) { this.light = light; }
public void execute() { light.on(); }
public void undo() { light.off(); }
}
// 关灯命令
class LightOffCommand implements Command {
private Light light;
public LightOffCommand(Light light) { this.light = light; }
public void execute() { light.off(); }
public void undo() { light.on(); }
}
// 开风扇命令
class FanOnCommand implements Command {
private Fan fan;
public FanOnCommand(Fan fan) { this.fan = fan; }
public void execute() { fan.on(); }
public void undo() { fan.off(); }
}
// 关风扇命令
class FanOffCommand implements Command {
private Fan fan;
public FanOffCommand(Fan fan) { this.fan = fan; }
public void execute() { fan.off(); }
public void undo() { fan.on(); }
}改造遥控器(Invoker)。
class RemoteControl {
private Command[] onCommands; // 存储"开"命令
private Command[] offCommands; // 存储"关"命令
private Command lastCommand; // 记录最后执行的命令(用于撤销)
public RemoteControl() {
onCommands = new Command[2]; // 假设有2个设备
offCommands = new Command[2];
}
// 设置按钮对应的命令
public void setCommand(int slot, Command onCmd, Command offCmd) {
onCommands[slot] = onCmd;
offCommands[slot] = offCmd;
}
// 按下"开"按钮
public void pressOnButton(int slot) {
onCommands[slot].execute();
lastCommand = onCommands[slot];
}
// 按下"关"按钮
public void pressOffButton(int slot) {
offCommands[slot].execute();
lastCommand = offCommands[slot];
}
// 撤销上一步操作
public void pressUndoButton() {
if (lastCommand != null) {
lastCommand.undo();
}
}
}客户端代码。
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建设备
Light light = new Light();
Fan fan = new Fan();
// 2. 创建命令对象
Command lightOn = new LightOnCommand(light);
Command lightOff = new LightOffCommand(light);
Command fanOn = new FanOnCommand(fan);
Command fanOff = new FanOffCommand(fan);
// 3. 配置遥控器
RemoteControl remote = new RemoteControl();
remote.setCommand(0, lightOn, lightOff); // 按钮0控制灯
remote.setCommand(1, fanOn, fanOff); // 按钮1控制风扇
// 4. 测试
remote.pressOnButton(0); // Light is ON
remote.pressOnButton(1); // Fan is ON
remote.pressUndoButton(); // Fan is OFF(撤销)
remote.pressOffButton(0); // Light is OFF
}
}如此遥控器和设备完全解耦。支持动态更换命令、撤销操作、宏命令(组合多个命令)。这个例子清晰地展示了命令模式如何通过封装行为来提升系统的灵活性和可扩展性。